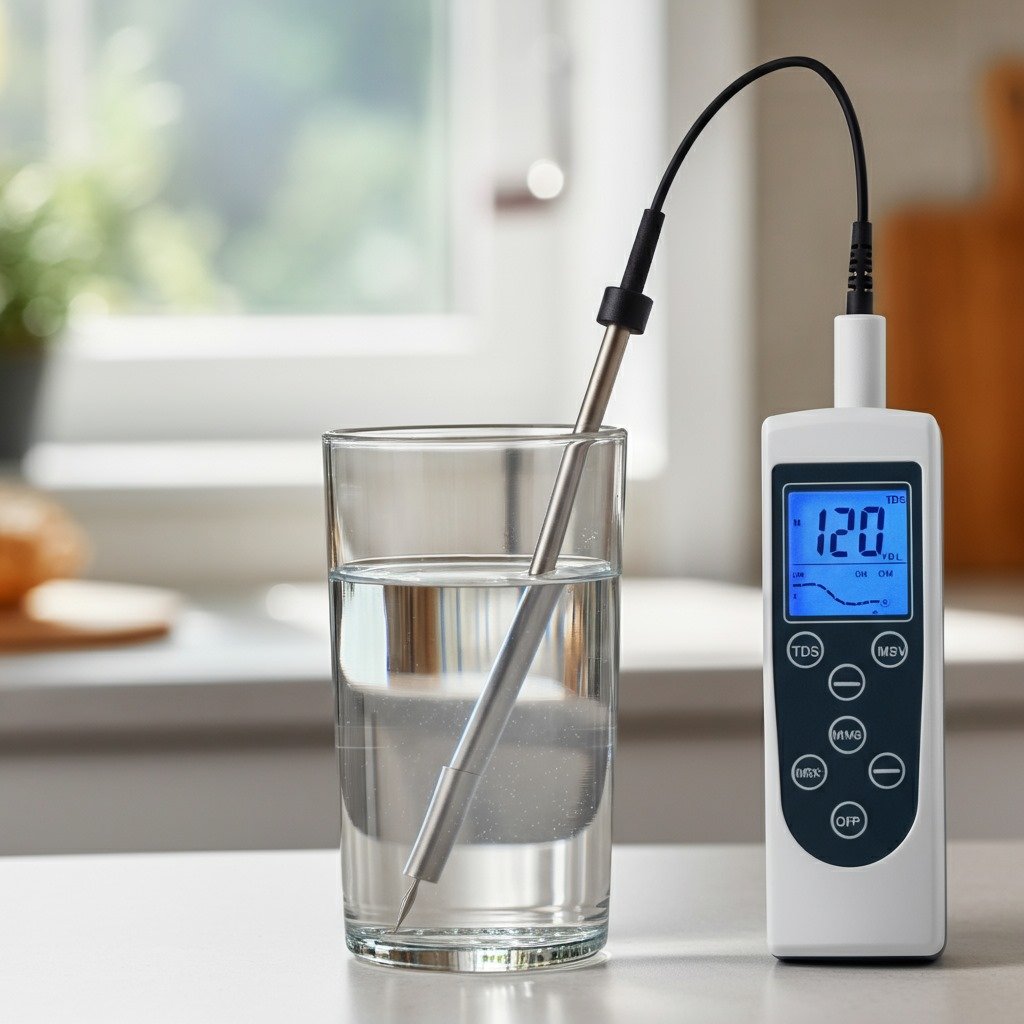
Water quality is essential for a healthy lifestyle, but it’s often overlooked in daily routines. From hidden contaminants to dissolved solids, the water you drink might contain impurities you can’t see.
A ZeroWater tester, designed specifically to measure Total Dissolved Solids (TDS), helps you monitor water purity easily at home.
This guide covers everything you need—from understanding TDS to step-by-step use and troubleshooting. By the end, you’ll know how to test water at home and ensure it’s safe for your family.
What Is a ZeroWater Tester?
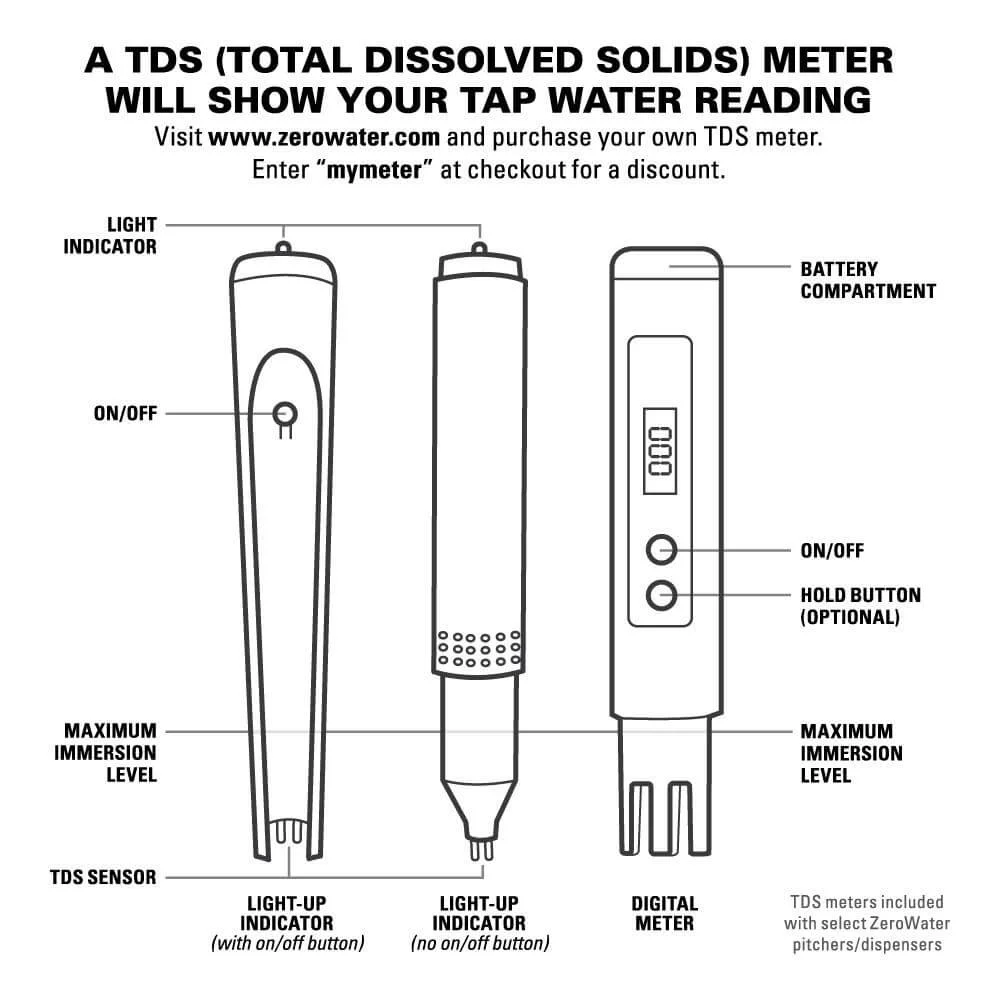
A ZeroWater tester is a compact, digital device that measures the amount of Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) in your water. These solids can include:
- Minerals like calcium or magnesium
- Harmful contaminants such as lead, arsenic, or pesticides
- Organic compounds and salts
While some dissolved solids improve taste, others can harm your health.
How Does the Zero Water Tester Work?
The tester features a digital screen and a probe. Simply dip the probe into water, and the TDS meter provides a reading in parts per million (ppm). The higher the reading, the more dissolved solids are in the water.
Pairing it with a ZeroWater filter, which aims for ZeroWater filter accuracy by reducing TDS to 0 ppm, gives you safe, clean drinking water.
Why Is Clean Water So Important?
Beyond just taste, water quality directly affects your health. Contaminated water may carry harmful substances.
With a ZeroWater tester, you can monitor water quality at home, giving you peace of mind with every glass.
What Comes in the Box?
When you buy a ZeroWater tester, you’ll typically find:
- TDS Tester – The main device
- Protective Cap – Keeps the probe safe when not in use
- Batteries – Pre-installed or separate
- User Manual – Explains how to use the device
- Optional Tools – May include calibration solution or cleaning items
Everything you need to begin testing your water right away.
How to Use a Zero Water Tester: Step-by-Step Instructions
Here’s a simple process for how to test water at home using your ZeroWater tester:
- Remove the Cap – Take off the protective cap to expose the probe.
- Rinse the Probe – Use distilled water to clean it before testing.
- Power On – Press the power button to turn on the display.
- Dip the Probe – Submerge only the probe (not the full device) into your water sample.
- Read the Display – Wait a few seconds until the reading stabilizes.
- Record the Result – Note the ppm value for future tracking.
Do’s and Don’ts for Accurate Testing
Do’s
✅ Use a clean container for samples
✅ Rinse the probe after every test
✅ Test water at room temperature
Don’ts
❌ Don’t submerge the entire device
❌ Avoid very hot or cold water
❌ Don’t skip probe cleaning
Pro Tip: For best results, take 3 readings of the same sample and average them.
Understanding TDS Readings
Here’s how to interpret the ppm results:
- 0 – 50 ppm: Excellent – ultra-pure water
- 50 – 150 ppm: Good – low contamination
- 150 – 300 ppm: Fair – moderate impurities
- 300+ ppm: Poor – unsafe drinking water
When to Replace Your Zero Water Filter?
Your ZeroWater filter should be replaced when the TDS reading exceeds 006 ppm. After this point, the filter may no longer remove contaminants effectively.
Common Issues & Troubleshooting
1. Tester Won’t Turn On
🔋 Check or replace the battery.
2. Reading Stuck at 000
💧 Make sure the probe is in water and clean off any buildup.
3. Display Malfunctioning
🧼 Gently wipe the screen. Refer to the manual for reset instructions if needed.
Best Practices for Long-Term Use
To keep your TDS meter reliable:
- Clean the Probe Regularly – Rinse with distilled water
- Calibrate Periodically – Especially if readings seem off
- Store Properly – Use the cap and keep it dry
- Test Weekly – Especially if your area has fluctuating water quality
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How accurate is the ZeroWater tester?
Very accurate when properly cleaned and used. It’s a trusted tool for checking water purity at home.
2. What TDS level is unsafe?
Above 300 ppm is typically considered unsafe for drinking.
3. Do I need to calibrate the tester?
It comes pre-calibrated, but you may calibrate it occasionally for continued accuracy.
Conclusion
Testing your water with a ZeroWater tester is easy, fast, and empowering. It gives you confidence that your drinking water is clean and healthy.
With this guide, you now know how to test water at home using a TDS meter, interpret the results, and keep your device accurate for years to come.
✅ Take control of your water quality—test your water today!
This blog was written based on deep research conducted by the Blogs by Nafayy team to ensure accurate and helpful information for our readers.
If you’re interested in reading more blogs like this, click here.
